Good Practice (GxP) audits are the cornerstone of regulatory compliance in the pharmaceutical and medical technology industries, ensuring the quality and safety of medicines and medical devices. Whether focused on GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice), GDP (Good Distribution Practice), GCP (Good Clinical Practice), GLP (Good Laboratory Practice) or GPvP (Good Pharmacovigilance Practice), they demand precise and accurate communication between the lead auditor and the host team. Given the global nature of the life science sector, quality assurance measures often involve assessing proprietary facilities or external suppliers in different countries. Language barriers can complicate this process, potentially causing delays or compliance risks. Drawing on our extensive experience supporting life science organisations across Europe with their language needs, in this article we highlight the vital role of professional audit interpreters. Whether your next audit is in Germany, France, Switzerland or another international location, you will learn best practices to ensure a successful outcome.
When Does a Pharmaceutical or Medical Device Company Need an Interpreter for Its GxP Audit?
GxP inspections and audits require precise, real-time communication, but challenges arise when they are conducted across borders. This is particularly the case when inspectors or auditors do not speak the local language or when key documentation is unavailable in their preferred language. In such scenarios, qualified interpreters provide indispensable linguistic support, facilitating accurate exchanges of highly complex and nuanced technical information. By bridging language gaps, they help prevent misinterpretations that could lead to delays, compliance risks or misrepresented findings.
Common Scenarios Requiring Interpreters
In international settings, quality assurance measures — such as inspections, monitoring visits, and audits — often pose multilingual communication challenges. Typical scenarios include:
- Internal Audits (First-Party or Self-Inspections)
When reviewing your own facilities in foreign locations, language barriers between your central inspection team and local staff can hinder effective communication. Self-inspections typically focus on ensuring alignment with industry-specific quality standards and your internal Quality Management Systems (QMS). Key tasks include examining manufacturing processes, verifying adherence to Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs), checking compliance with company-specific quality benchmarks, and assessing readiness for inspections by regulatory authorities. Professional linguists enable seamless communication, ensuring findings and recommendations are accurately conveyed to all stakeholders. - Supplier Qualification Audits
When assessing your external suppliers or contract manufacturing organisations (CMOs), whether new or existing, in other countries, effective communication is critical to confirm their compliance with GxP standards. These measures may involve evaluating a variety of pharmaceutical manufacturers, such as suppliers of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), key starting materials (KSMs) or excipients, as well as a range of service providers, such as distributors, contract testing laboratories or processing sites (e.g., micronisation, sterilisation or radiation). Skilled linguists ensure that complex technical discussions — such as those on the specifics of pharmaceutical production processes, compliance with GMP standards, and adherence to applicable ISO norms — are accurately translated, enabling a clear understanding of the supplier’s capabilities. - Clinical Trial Monitoring Visits and Audits
When reviewing clinical trial sites in international locations, effective communication is essential to ensure compliance with GCP guidelines. These activities often involve detailed reviews of trial documentation (e.g., investigator site files, patient consent forms, source data verification records). Professional linguists facilitate accurate exchanges during discussions about protocol adherence, safety reporting, and data integrity, ensuring that all parties understand trial requirements and regulatory expectations.
Audit Components and the Role of the Interpreter
A typical audit follows a structured agenda, covering both a facility inspection and a document review. TA typical audit follows a structured agenda, covering both a facility inspection and a document review. The interpreter plays an essential role in facilitating effective, accurate exchanges of information throughout these activities:
- Opening Meeting
Supports communication at the opening meeting to ensure the scope, objectives, and methodologies are understood.
- Facility Walkthrough
Facilitates discussions during the inspection of physical premises, equipment, and operational practices. Provides accurate translations of questions and responses about production workflows, cleanliness measures, and equipment maintenance, preventing misunderstandings that could impact the evaluation.
- Interviews with Key Personnel
Enables detailed conversations with managers and staff about quality control processes, adherence to SOPs, and staff qualifications. Ensures technical details are clearly conveyed and fully understood by all parties.
- Document Review
Delivers sight translation of essential records, such as SOPs, batch production logs, maintenance schedules, and process workflows. Clarifies technical terminology and the intent of documented processes to ensure compliance with regulatory standards.
- Closing Meeting
Interprets feedback, preliminary findings, and next steps to foster alignment and mutual understanding.
How Is Information Translated at Each Stage of the Agenda?
Professionally trained interpreters use various modes to ensure seamless communication during different agenda activities:
Simultaneous Interpreting
The interpreter listens to the speaker and provides real-time interpretation with a slight delay. This mode saves time by maintaining the natural flow of communication and is particularly suited for formal sessions or large-group discussions.
Consecutive Interpreting
The interpreter listens to a segment of speech, takes notes if necessary, and delivers the consecutive interpretation during pauses. This approach allows for detailed and accurate interpretation, making it ideal for technical conversations and smaller, interactive discussions.
Sight Translation
The interpreter reads a written document and orally translates it on the spot. This approach provides immediate access to critical information without requiring prior translation, ensuring all key materials are clearly understood.
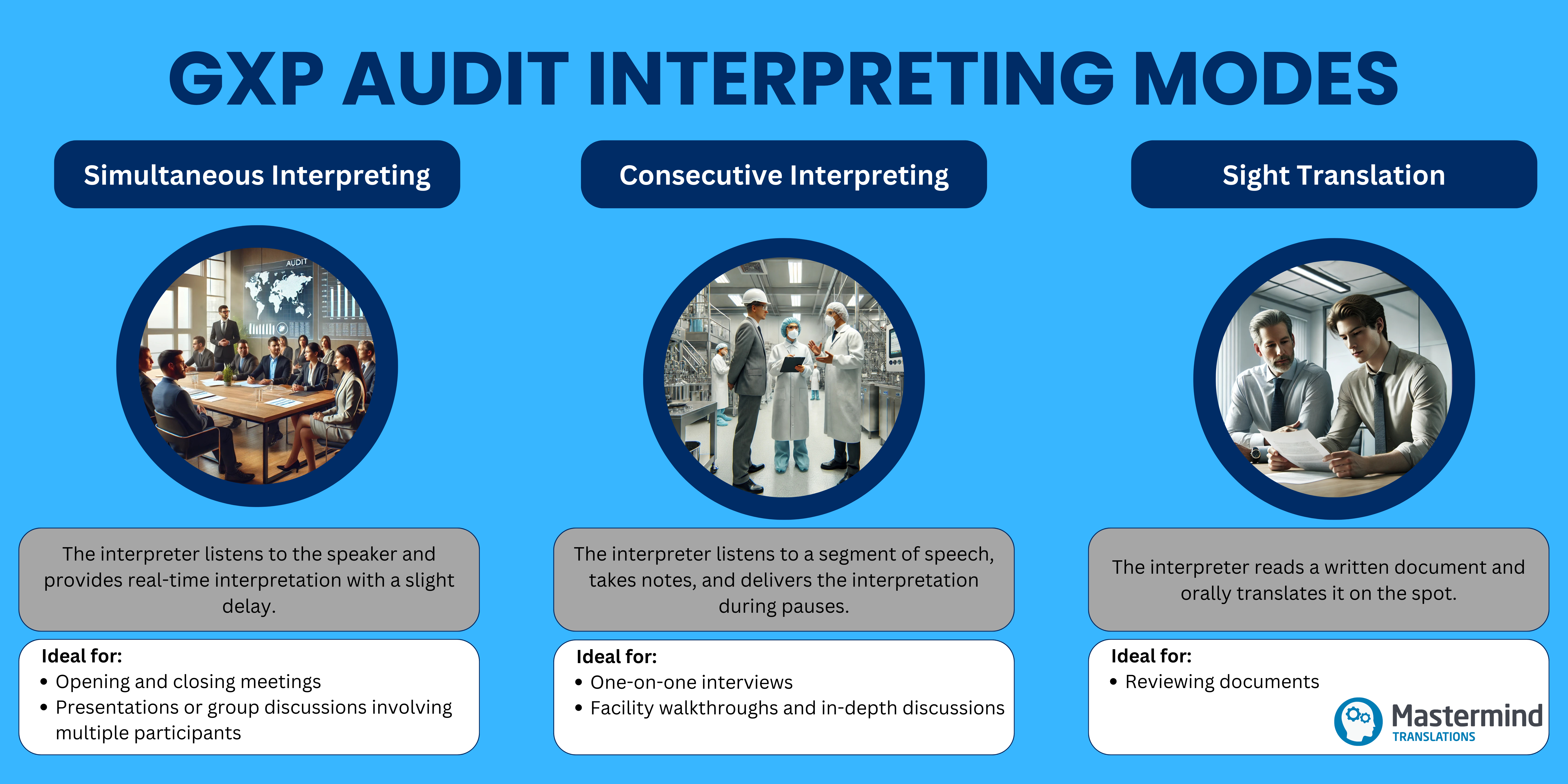
By using the most appropriate mode for each stage, professional interpreters minimise disruptions, maintain the flow of communication, and enhance the efficiency of the process.
How to Book a Professional Interpreter for Your Next GMP Inspection or Audit?
Securing the right interpreter requires careful planning and coordination. Follow these steps:
- Define Your Needs
- Identify the languages required, the type of audit, and any technical or regulatory specifics that the interpreter should understand.
- Choose a Specialised Agency
- Select an interpreting service provider with expertise in the medical device and pharmaceutical industries and a proven track record of supporting international audits. The expertise of your Language Service Provider (LSP) will ensure that interpreters are highly qualified and well-prepared. If this is your first experience working with an interpreter, consider a discovery meeting to better understand how this process works.
- Provide Relevant Information in Advance
- Early engagement ensures availability and adequate preparation time. Share key details, such as the agenda, technical documents, and contact information.
Best Practices for Engaging Audit Interpreters
As a specialised life science translation service provider, we manage every aspect of providing professional translators and interpreters for audits, ensuring that all linguistic aspects of your audit are expertly managed. Here are the key best practices to consider:
- Rely on Industry-Specific Expertise
Work with an LSP that provides interpreters with proven experience in the pharmaceutical and medical technology sectors. Their life science background ensures technical accuracy and fluency in regulatory terminology. - Leverage Vetted Language Skills
A trusted LSP ensures that interpreters are professionally trained in all interpreting modes and can adapt seamlessly to the demands of various parts of the agenda. Each linguist should be rigorously vetted to meet necessary quality criteria. - Ensure Advanced Preparation
Share relevant materials, such as agendas, glossaries, and technical documents, with your LSP in advance. Your LSP will coordinate this preparation, ensuring linguists are fully briefed and ready to deliver precise communication tailored to your needs. - Safeguard Confidentiality
A reputable LSP guarantees strict confidentiality standards through robust non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) and secure handling of commercially sensitive information. - Benefit from Logistics Management
From selecting qualified interpreters to handling schedules, travel, and on-site coordination at the manufacturing site, an LSP experienced in audit support will remove the administrative burden from your team.